The Latin Grill: Much More Than Meat on a Flat Top
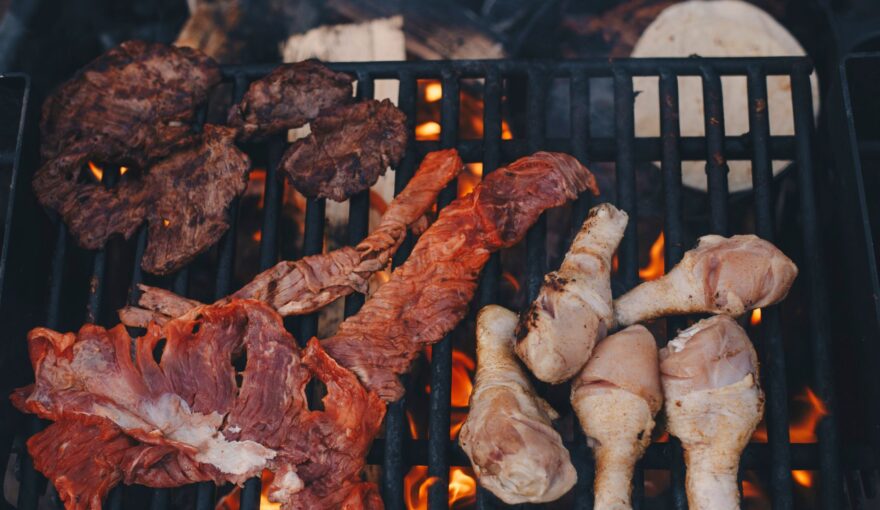
In Latin cuisine, grilling is not simply a way to cook food—it is a cultural language. Across Mexico, Central America, and South America, the grill represents tradition, patience, and respect for ingredients. The flavor that comes from a true Latin grill cannot be rushed or improvised, and it goes far beyond placing meat over heat.
At Azúcar, we treat the grill as a craft, not a shortcut.
Mexico: fire, marinades, and balance
In Mexican grilling traditions, flavor begins long before the meat touches the flame. Marinades made with citrus, garlic, herbs, and dried chiles are designed not to mask the protein, but to enhance it. Grilling is done with careful attention to heat zones, allowing the meat to caramelize without drying out.
The result is a balance of smokiness, acidity, and natural meat flavor—a technique that requires experience, not guesswork.
Central America: simplicity that highlights quality
Central American grilling is rooted in simplicity and ingredient quality. The focus is on well-seasoned meats cooked over live fire, often paired with plantains, cassava, or corn-based sides. Here, grilling is about restraint: letting the fire bring out the essence of the ingredient instead of overpowering it.
This style demands excellent sourcing and precise timing. When done correctly, the flavor is clean, deep, and unmistakably authentic.
South America: mastery of the open flame
South American asado traditions elevate grilling to an art form. Cuts are selected specifically for slow grilling, allowing fat to render gradually and create rich, layered flavor. Temperature control is critical, and cooking times are respected—never rushed.
This approach transforms grilling into a slow, deliberate process where texture, aroma, and taste develop together.
Why the Latin grill tastes different
What sets Latin grilling apart is intention. The fire is not just a heat source; it is part of the recipe. Each region understands how flame interacts with marinades, fats, and natural juices, creating flavors that cannot be replicated on a flat top or in a pan.
True grilling takes time, experience, and consistency. There are no shortcuts.
A grill guided by tradition
At Azúcar, our grill reflects these traditions. Every cut is prepared with purpose, every flame carefully controlled. This commitment ensures that each dish delivers the depth, aroma, and texture that define authentic Latin cuisine.
Choosing where to dine is choosing how your food is treated—from the moment it’s seasoned to the moment it reaches your table. Experience a grill that respects tradition and delivers flavor the way it was meant to be enjoyed.
At Azúcar, the grill is not just a cooking method—it’s a promise of authenticity.